Erik Hjelmvik
,
Wednesday, 26 April 2023 08:50:00 (UTC/GMT)
I analyzed a PCAP file from a sandbox execution of the Evil Extractor stealer malware earlier today. This stealer collects credentials and files of interest from the victim’s computer and exfiltrates them to an FTP server. It is designed to autonomously collect and exfiltrate data rather than receiving commands from an operator through a command-and-control channel. The EvilExtractor creators market this feature as a “golden bullet”.
Real hackers don’t use reverse shells right? If you have only one bullet, would you waste with reverse shell? Try Evil Extractor to have golden bullet.
I downloaded the Evil Extractor capture file from
Triage to a Windows Sandbox environment, to avoid accidentally infecting my computer when extracting artifacts from the PCAP.
I then opened it up in the free version of NetworkMiner.
NetworkMiner shows that after checking its public IP on ipinfo.io EvilExtractor makes an unencrypted HTTP connection to a web server on 193.42.33.232 to download KK2023.zip. This zip archive contains a file called “Lst.exe” which is used to steal browser data, cookies and credentials according to Fortinet.
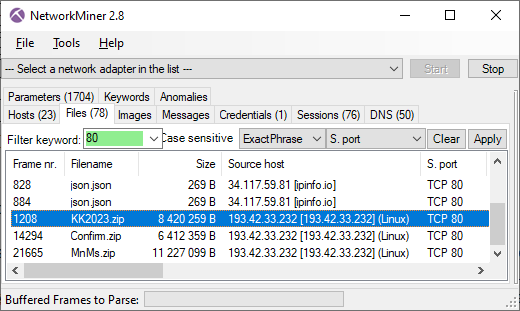
Image: Files downloaded from TCP port 80
Twenty seconds later an FTP connection is established to 89.116.53.55 on TCP port 21. The username and password used to authenticate to the FTP server was “u999382941” and “Test1234”.
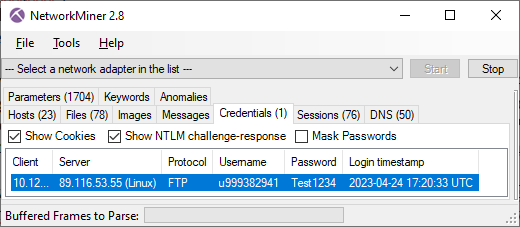
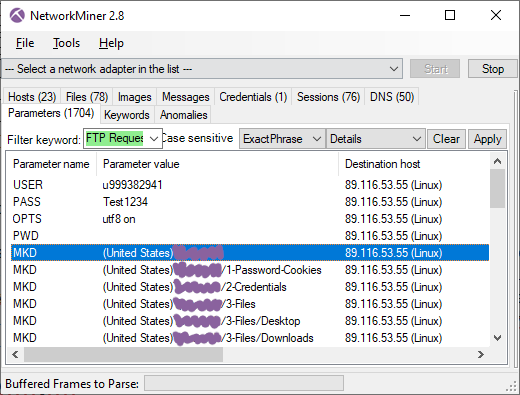
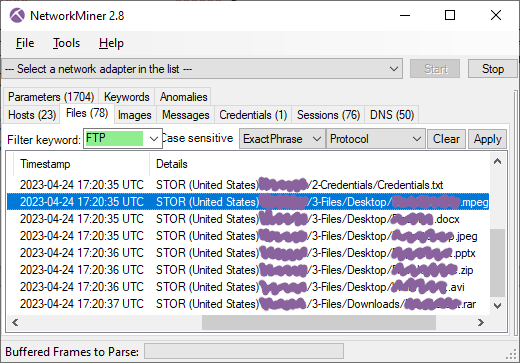
On the FTP server EvilExtractor creates a directory named after the country and hostname of the victim's PC, such as “(Sweden)DESKTOP-VV03LJ”, in which it creates the following three sub directories:
- 1-Password-Cookies
- 2-Credentials
- 3-Files
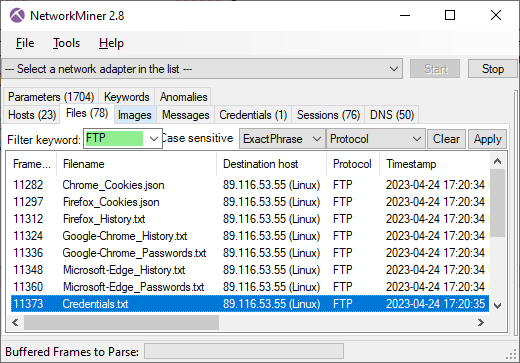
After uploading browser cookies, browser history and cached passwords from Chrome, Firefox and Edge to the “1-Password-Cookies” directory EvilExtractor sends a file called “Credentials.txt” to the “2-Credentials” directory. The contents of this text file looks something like this:
Public IP: [redacted]
Location: [lat],[long]
Computer Name: [redacted]
Username: Admin
RAM: 4 GB
OS Name: Microsoft Windows 10 Pro
OS Bit: 64-bit
Keyboard Language: en-US
GPU: [redacted]
CPU: Intel [redacted]
MAC Address: [redacted]
Extracted WIFI: [redacted]
The stealer also exfiltrates files with mpeg, docx, jpeg, pptx, zip, avi and rar extensions from the victim PC to the “3-Files” directory on the FTP server.
The directory structure of the victim’s PC is maintained on the FTP server, so that files from the victim's desktop end up in a folder called “Desktop” on the FTP server.
The stealer later downloaded a keylogger module (Confirm.zip) and a webcam module (MnMs.zip), but no additional data was exfiltrated from this particular victim PC after that point.
IOC List
- Web server: 193.42.33.232:80
- FTP server: 89.116.53.55:21
- EvilExtractor: 9650ac3a9de8d51fddab092c7956bdae
- KK2023.zip: f07b919ff71fb33ee0f77e9e02c5445b
- Lst.exe: 163d4e2d75f8ce6c838bab888bf9629c
- Confirm.zip: 30532a6121cb33afc04eea2b8dcea461
- Confirm.exe: 0c18c4669e7ca7e4d21974ddcd24fdca
- MnMs.zip: bda0bda512d3e2a81fc9e4cf393091eb
- MnMs.exe: fb970c4367609860c2e5b17737a9f460
Users with an account on Triage can download the analyzed PCAP file from here:
https://tria.ge/230424-vv9wvsfb2v/behavioral2
Update 2023-04-27
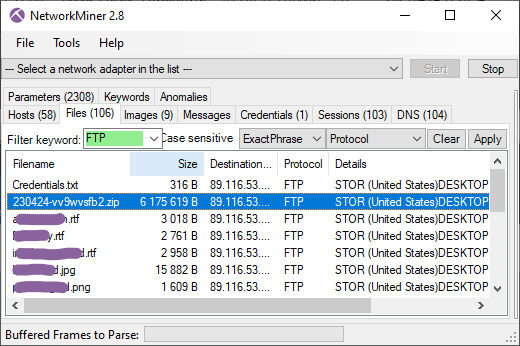
Jane tweeted a link to an execution of this same sample on ANY.RUN. This execution showed very similar results as the one on Triage, but with an interesting twist. Not only did the ANY.RUN execution exfiltrate images and documents from the Desktop and Downloads folders, it also exfiltrated “vv9wvsfb2v_pw_infected.zip”, which contained the EvilExtractor EXE file that was being run!
The PCAP from the ANY.RUN execution can be downloaded from here:
https://app.any.run/tasks/43a11a79-4d1f-406c-86d7-158efb5ede01/
Posted by Erik Hjelmvik on Wednesday, 26 April 2023 08:50:00 (UTC/GMT)
Tags: #FTP
#NetworkMiner
#Sandbox
#Triage
#ANY.RUN










