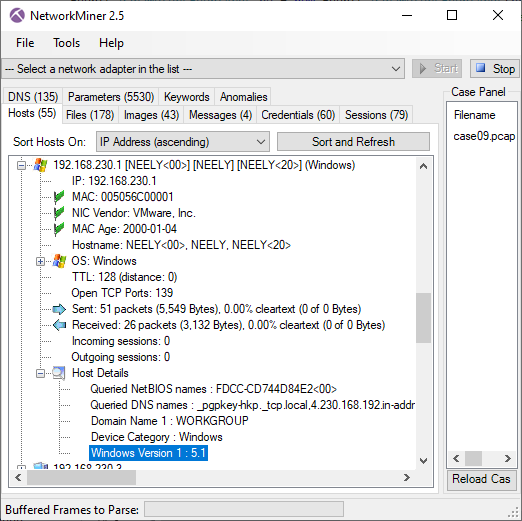
NetworkMiner 2.7.3 Released

NetworkMiner now extracts meterpreter payloads from reverse shells and performs offline lookups of JA3 hashes and TLS certificates. Our commercial tool, NetworkMiner Professional, additionally comes with a packet carver that extracts network packets from memory dumps.
Extraction of Meterpreter Payloads
NetworkMiner 2.7.3 supports extraction of meterpreter DLL payloads from reverse shell TCP sessions deployed with Metasploit. The free version of NetworkMiner will try to extract the meterpreter DLL from TCP sessions going to "poker-hand ports" commonly used for meterpreter sessions, such as 3333, 4444, 5555, etc. The port-independent protocol detection feature available in NetworkMiner Professional additionally enables extraction of meterpreter DLLs regardless which LPORT the attacker specifies when deploying the reverse shell.
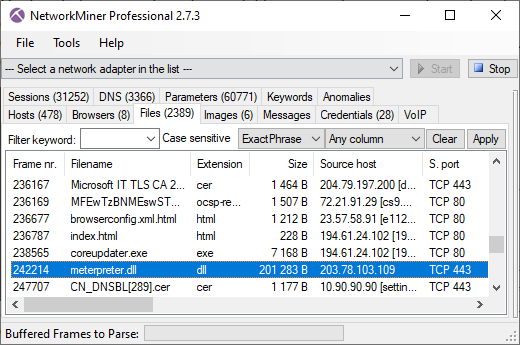
Image: Meterpreter DLL extracted from DFIR Madness' case001.pcap
Packet Carving in NetworkMiner Professional
If you try to open anything other than a PCAP, PcapNG or ETL file in NetworkMiner Professional, then you'll be presented with an option to carve packets from the opened file as of this release.
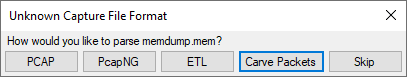
The packet carver can extract packets from any structured or unstructured data, such as memory dumps and proprietary packet capture formats. NetworkMiner Pro's carver is a simplified version of the packet carving feature in CapLoader.
Loading the 1GB "memdump.mem" from Ali Hadi's Challenge #1 - Web Server Case into NetworkMiner Professional takes roughly five seconds, during which 612 packets get extracted.
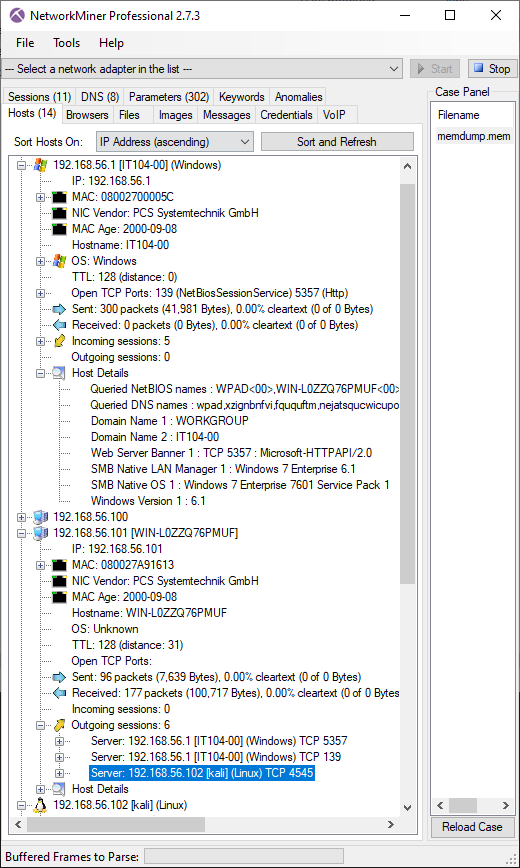
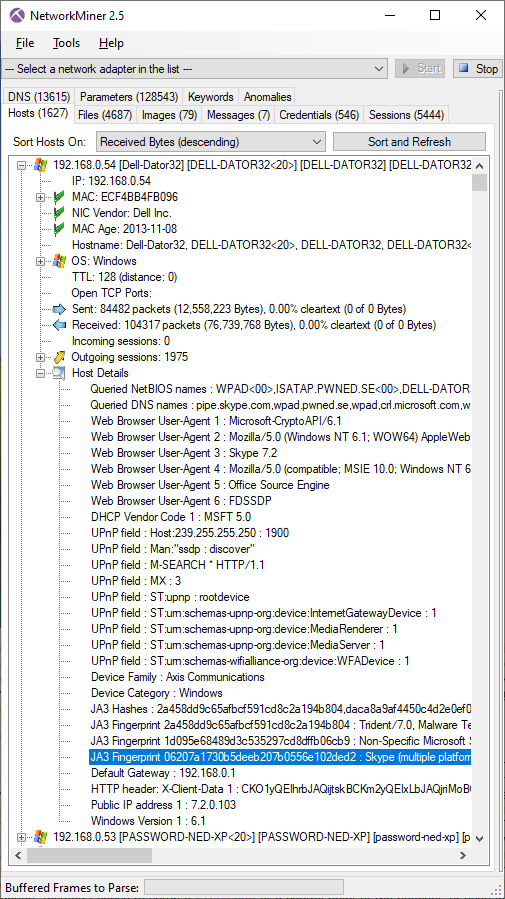
Image: Information about network hosts carved from memory dump
In this scenario the memory was dumped on the 192.168.56.101 host, which NetworkMiner identifies as "WIN-L0ZZQ76PMUF". The carved packets also indicate that this computer had an outgoing TCP connection to 192.168.56.102, which appears to be a Linux machine called "kali". As you can see in the screenshot, the packets carved from the memory dump also reveal a great deal about other hosts on the network, such as the 192.168.56.1 host, which seems to be a Windows 7 machine called "IT104-00".
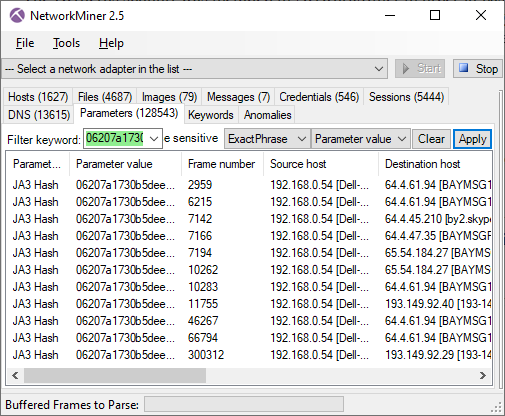
Offline Matching of JA3 and X.509 hashes
NetworkMiner 2.7.3 comes with a local copy of the SSL Certificate and JA3 Fingerprint Blacklists from the awesome abuse.ch project. JA3 hashes and extracted X.509 certificates are matched against these lists in order to see if they are associated with any piece of malware or botnet.
Here's one example showing the default Cobalt Strike certificate being identified as "AKBuilder C&C", since that's how it is listed in abuse.ch's SSL certificate database.
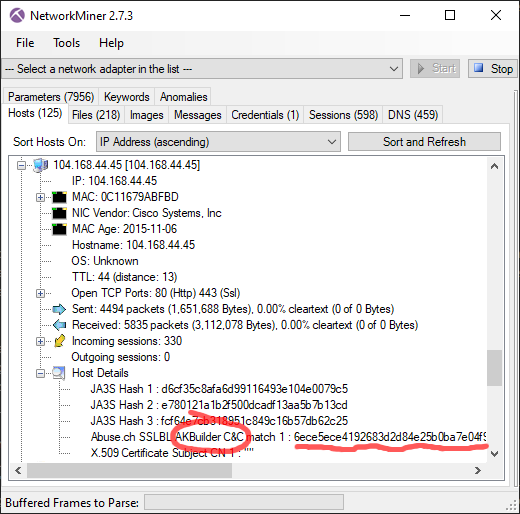
Image: Cobalt Strike's default certificate identified as "AKBuilder C&C"
PCAP: Cobalt Strike PCAP from malware-traffic-analysis.net
The port-independent protocol detection feature in NetworkMiner Professional additionally enables X.509 certificates to be extracted even from non-standard TLS ports, such as this certificate, which is identified as "BitRAT" with help of the abuse.ch certificate block-list.
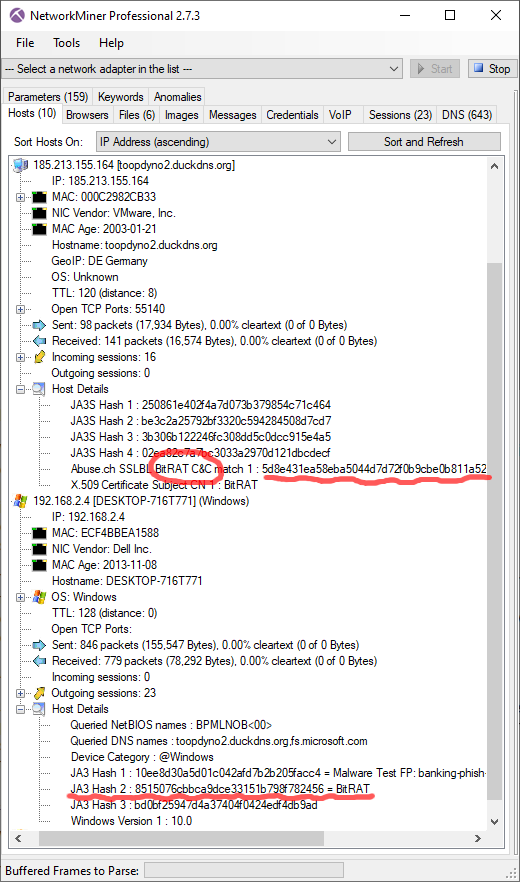
Image: Both X.509 certificate and JA3 hash identified as BitRAT
PCAP: BitRAT PCAP from Joe Sandbox
The client's JA3 hash 8515076cbbca9dce33151b798f782456 is also associated with BitRAT according to abuse.ch.
DBSBL Lookup Detection
DNSBL services are used by servers handling incoming email to verify that the sender's IP address isn't a known SPAM sender and that it isn't from a network that shouldn't be sending emails.
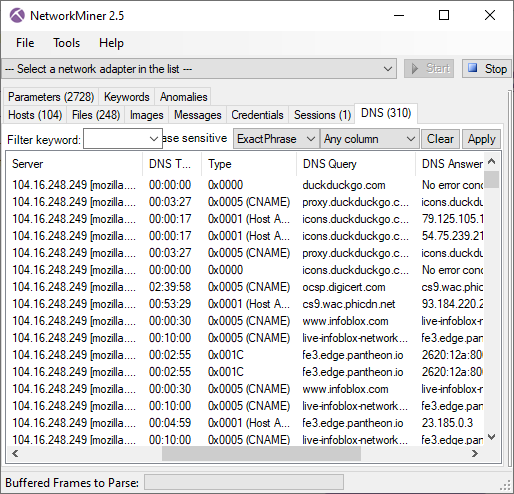
But DNSBL services can also be used by malware and botnets, such as TrickBot and Emotet, to verify that the public IP of a victim is allowed to send emails and that it hasn't already been blacklisted for sending SPAM. We have therefore decided to add DNSBL lookups to the Host Details section in NetworkMiner 2.7.3.
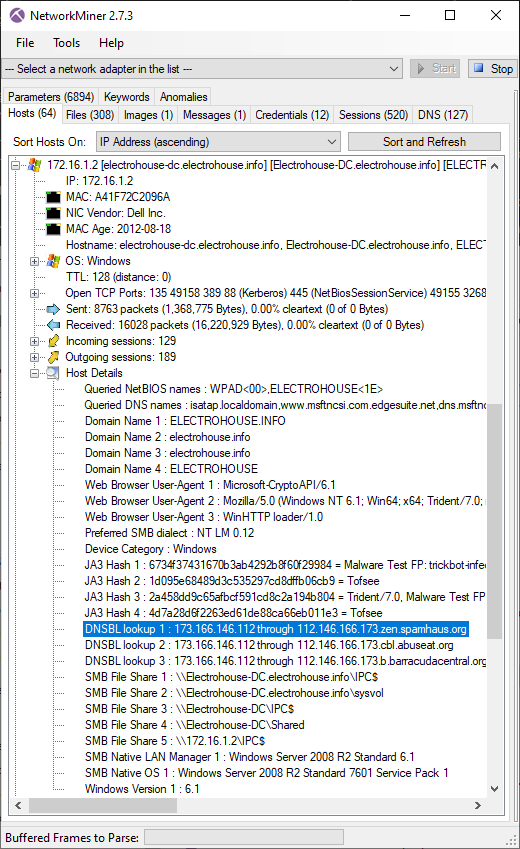
Image: TrickBot victim checks if its public IP is blocked by DNSBL services
PCAP: TrickBot PCAP from malware-traffic-analysis.net
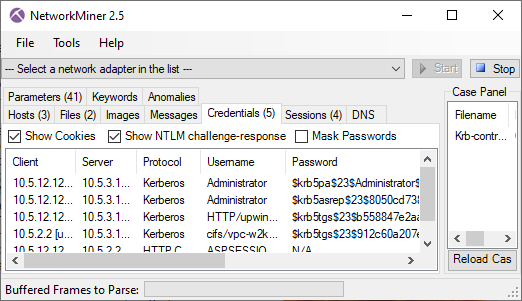
DNSBL lookups are also logged to the "Parameters" tab of NetworkMiner.
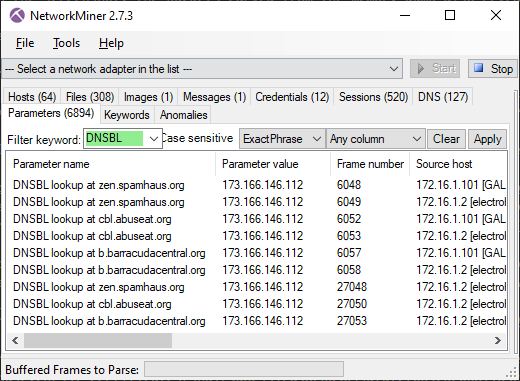
Image: NetworkMiner's Parameters tab with "DNSBL" filter
PCAP: TrickBot PCAP from malware-traffic-analysis.net
Additional Features and Updates
We'd also like to mention some additional new features, bug fixes and improvements that have been included in this new release.
- Support for HTTP CONNECT request method to extract artifacts like X.509 certificates and JA3 hashes from HTTPS traffic passing through a web proxy.
- Traffic to TCP ports 3000 and 8000 are now configured to be parsed as HTTP by default in order to handle WEBrick traffic.
- Improved extraction of SMTP credentials.
- JA3 hashes were previously incorrect for clients that supported more than one EC point format (RFC 8422). This has now been fixed.
- Support for SLL2 (Linux cooked capture v2) frames.
- Improved handling of concurrent GUI events, for example when poking around in the "Hosts" tab while loading a PCAP file or doing live sniffing.
- NetworkMiner's GUI no longer reloads between each PCAP file when multiple files are loaded at once.
New Features in NetworkMiner Professional
We have also added a few new features exclusively to NetworkMiner Professional, which is the commercial version of NetworkMiner. Apart from the packet carver feature, mentioned earlier in this blog post, we've also updated the collection of OSINT lookup services available in the GUI. One of the newly added services is Ryan Benson's unfurl, which picks apart URLs to reveal data that might have been encoded into a complex URL. The unfurl lookup can be found by right-clicking an URL in NetworkMiner Professional's "Browsers" tab and selecting the "Lookup URL" sub menu.
Other OSINT services that we've added are FileScan.IO and JoeSandbox lookups of extracted files. These lookups can be performed by right clicking a file in the "Files" tab and opening the sub-menu called "Lookup Hash".
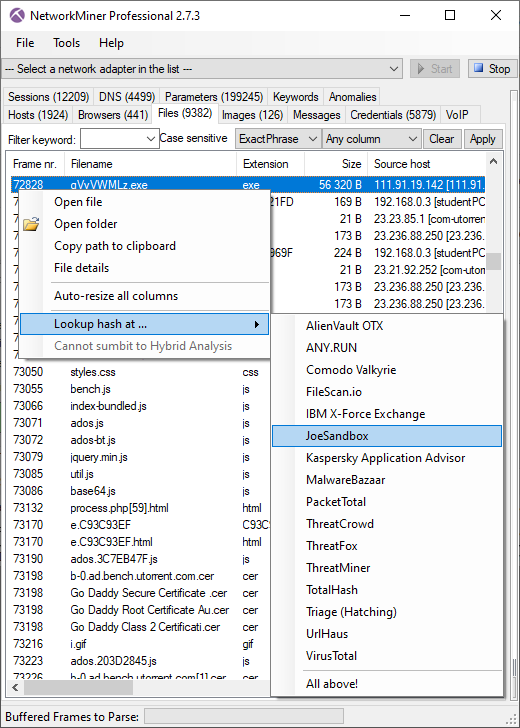
Image: OSINT lookup of an EXE file extracted from network traffic
The command-line version of NetworkMiner Professional, NetworkMinerCLI, has also been updated to allow extracted information to be printed directly on standard output instead of logging everything to files. Here is an example showing this feature while running NetworkMinerCLI in Linux (with help of Mono):
"s2Fmok83x.zip.html","ba2ef33c7aef593f95d261b6f4406b39"
"nexus.officeapps.live.com.cer","373ccffe30d3477867642abab723a351"
"Microsoft RSA TLS CA 01.cer","806f1c72f6d67c9c114eff43d3d84100"
"nexusrules.officeapps.live.c.cer","4c08442740cb020d457a5df16be406ff"
"Microsoft RSA TLS CA 02.cer","65d17ecae5798c79db8e840fe98a53b9"
"6537991.dat.exe","124207bc9c64e20e114bcaeabde12a4e"
"6537991.dat.exe","ca7ef367c935182a40a95b9ad8b95f42"
"6537991.dat.exe","a9a8366fa6be54b45ca04192ca217b75"
[...]
The command above extracts files from a PCAP file, which contains traffic from a Windows PC infected with Qbot. The "-w" switch specifies the output directory for the files extracted from network traffic, and the "-X FileInfos" specifies that metadata for these files should be sent to STDOUT instead of being written to log files. The cut utility was used to show only the filename (column 5) and MD5 hash (column 9) of the file info output.
The MD5 hashes of the extracted files confirm that this is indeed a Qbot infection:
- 124207bc9c64e20e114bcaeabde12a4e (VT)
- ca7ef367c935182a40a95b9ad8b95f42 (VT)
- a9a8366fa6be54b45ca04192ca217b75 (VT)
NetworkMinerCLI previously printed some information about the parsing process to STDOUT. That output has now been moved to STDERR in order to provide the "-X [type]" output with exclusive access to STDOUT.
Credits
We'd like to thank Michael Taggart for noticing that NetworkMiner previously failed to parse HTTP traffic to ports 3000 and 8000.
Upgrading to Version 2.7.3
Users who have purchased NetworkMiner Professional can download a free update to version 2.7.3 from our customer portal, or use the “Help > Check for Updates” feature. Those who instead prefer to use the free and open source version can grab the latest version of NetworkMiner from the official NetworkMiner page.
Posted by Erik Hjelmvik on Monday, 04 April 2022 06:52:00 (UTC/GMT)
Tags: #NetworkMiner #carve #JA3 #X.509 #CobaltStrike #Cobalt Strike #TrickBot #Emotet #PIPI #Protocol Detection #OSINT #NetworkMinerCLI